
Tidal energy reduces dependency on oil reserves from other countries.Its predictability makes it easy to integrate into existing power grids.Tides are predictable and go in and out twice a day, making it easy to manage positive spikes.Those in favor of the use of tidal energy stations site these advantages: Barrages have high infrastructure cost and are lengthy projects.

#Tidal barrage install#

Barrages change the intertidal zone plant and animal life must adapt or move to a new location which impacts the ecosystem of the area.Barrages block navigation even when locks are installed it is slow and more costly.Barrages impede fish migration fish are instinctively obliged to swim through the turbines of the barrages at least twice in the migrating route and the mortality rate is about six percent.
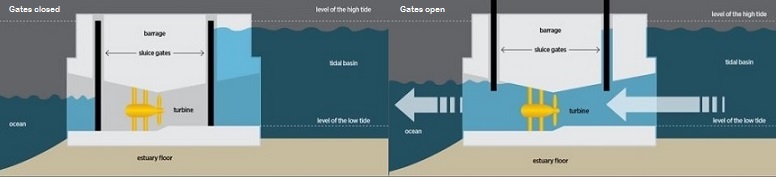
Those opposed to constructing tidal barrages site the following reasons: The use of tidal energy has both advantages and disadvantages. Currently, European and Asian countries are constructing hydroelectric tidal barrage plants of varying capacities. This tidal barrage boasts a 20 megawatt turbine and is the only commercial tidal barrage in North America. The second large tidal barrage was built in 1982 and is located at Annapolis Royale, Nova Scotia, Canada. It has 24 turbines reaching a peak rating of 240 Megawatts of power enough power to supply. It opened in 1966 and is the largest tidal power station in the world in terms of installed capacity. The first actual tidal wave hydropower facility was built in Brittany, France on the estuary of the Rance River. Waterwheels and similar devices eventually gave way to the more efficient bulb-type hydroelectric turbine-generator combination. These early systems are early methods of how tidal energy works. The Woodbridge Tide Mill built in 1170 in Suffolk, England is an example of this type of mill. As the tide fell, the stored water was released to turn a water wheel. The water flowed into the reservoir through a one-way gate which automatically closed. The use of waterpower can be traced back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, the Turpan water system in ancient China and the Qanat system in ancient Persia.Įarly methods of the use of tidal energy were dams with a sluice spanning a tidal inlet. For centuries people have used water to produce energy, from mills for processing grains to irrigation systems for crops. They work the same as the tidal barrage as the tide rises, the lagoon fills and as the tide falls, the water turns the turbines which generate energy. Tidal lagoons are self contained structures sectioned off from the sea. They are similar to barrages but are lower in cost and environmental impact. Tidal lagoons are the third method of how tidal energy works. As the tide goes back out, turbines in the gates open and as the water flows through them, generates energy.

When the tide stops, the gates close and trap the water. As the tides come in, the water is collected into the basin through the dam. The range between low and high tide must exceed five meters (16.4 feet) for the barrage to work. Tidal barrages, the second method of how tidal energy works, are similar to dams, but are much bigger as they are built across a bay or estuary. This type of system works best in strong tidal zones.
#Tidal barrage generator#
The water current turns the blades which activate a generator which produces electricity. They use the same technology as windmills, but the blades are stronger and shorter. Tidal turbines are much like underwater windmills. There are three ways to harness the power of the tides. Tidal energy is produced with the changing levels of the sea the tide moving in and out. Credit: eriwst via Flickr How Tidal Energy Works


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
